
Quinoa
On this page
Grown in the Andes for over 7000 years, the last two decades have seen an explosion in popularity for quinoa all over the world.
Containing all nine essential amino acids, as well as being gluten free, high in fibre, and packed full of other important vitamins and minerals, quinoa has become a popular alternative to cereal grains like rice and wheat.
The new-found popularity of this pseudocereal (a seed eaten like a grain but not from a grass plant) led to crop prices tripling between 2006 and 2013, but prices have now dropped.
Quinoa is a member of the amaranth family (Amaranthaceae), which also contains beetroot, chard (Beta vulgaris) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea).
Plant description
Quinoa is an annual plant that can grow up to 2 metres tall. It has wide hairy leaves growing alternately from a woody steam which can be green, red, or purple depending on the cultivated variety (cultivar). At the top of the stem are panicles, clusters of small flowers that branch off the main stem. Flowers can be red to light purple and orange. The seeds are about 2 mm in diameter, and, depending on the cultivar, white, red or black.



Plant uses
Food and drink
When boiled, quinoa seeds are used in stews and salads, as well as replacement for cereal crops, like oat and wheat.
Quinoa can be ground into flour, which can then be used for cooking and baking.
Health
Cooked quinoa is a good source of iron, zinc and magnesium, as well as dietary fibre, manganese and phosphorus.
Quinoa contains all nine essential amino acids, making it a complete protein.
Materials and fuels
Quinoa has been used as part of animal feed in South America.
Did you know?
Quinoa is sometimes referred to as a pseudocereal, as it produces a seed similar to cereal grains, but isn’t a member of the grass family.
Quinoa was first cultivated and grown for animal feed, later becoming a staple food crop in the Lake Titicaca basin across Bolivia and Peru.
There are around 3000 varieties of quinoa, including ‘Cherry Vanilla’, ‘Bright Brilliant’ and ‘Bastille’.
The species name, quinoa, comes from the Spanish spelling of the Quechua name of the plant, kinua. The genus name, Chenopodium, means goosefoot, referring to the shape of the leaves.
Where in the world?
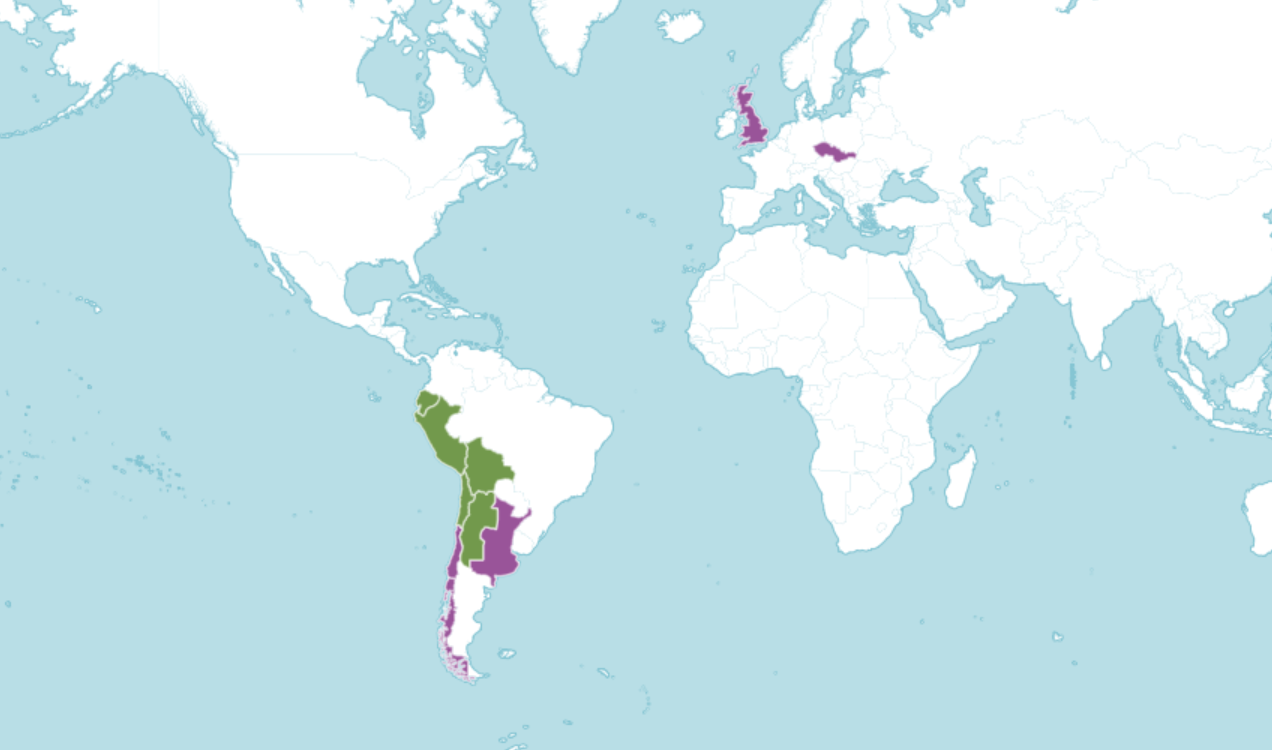
Grows anywhere between 4500m down to sea level in a wide range of environmental conditions, but prefers cool climates.
Our work
To secure the future of our food in a world with a growing population and changing climate, we need to protect the wild cousins of our commonly eaten and used plants, like quinoa.
These crop wild relatives are a source of valuable genetic diversity and useful traits which could help breeders develop new and improved crops that are more resilient to the impacts of climate change, like extreme temperatures or pests and diseases.
Kew scientists have been working alongside the Global Crop Diversity Trust on a global project which has involved collecting seeds from the wild relatives of quinoa, and storing them in our Millennium Seed Bank to conserve them for future generations.





