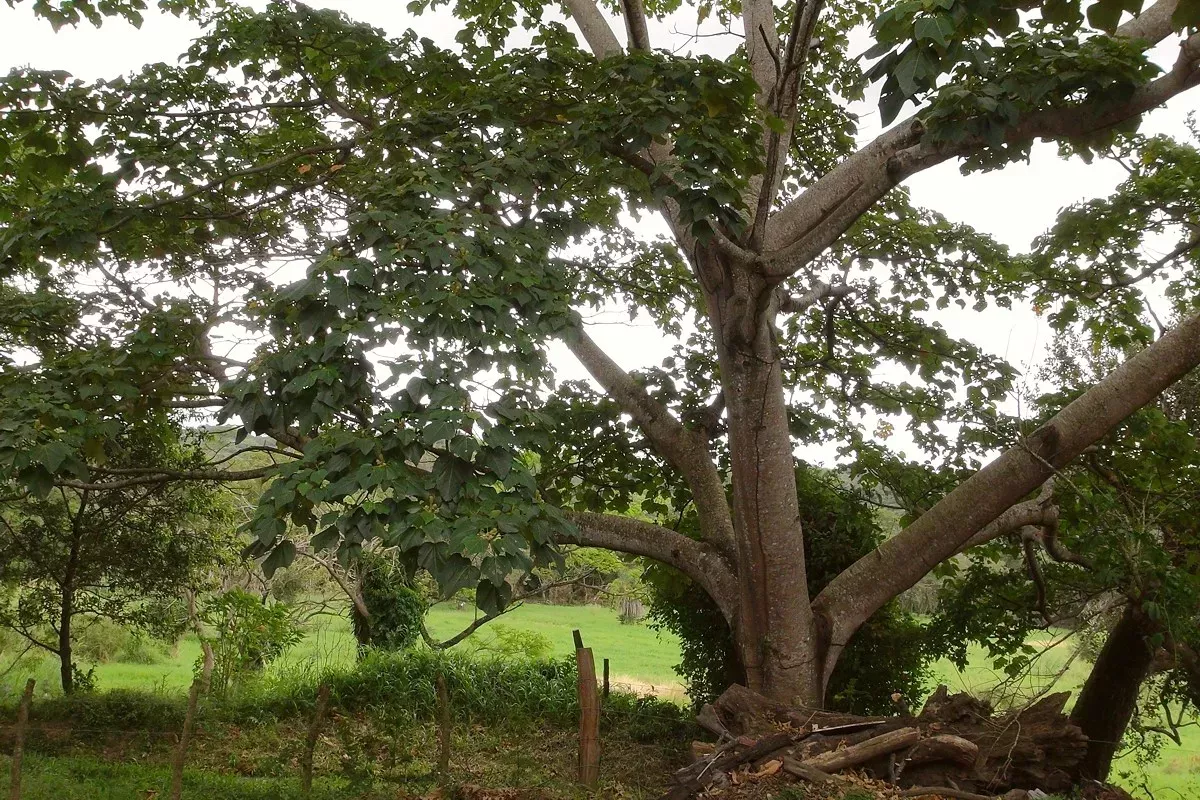
Balsa tree
Valued across the world for its strong but light wood, the balsa tree is native to the rainforests of South America.
Over 95% of balsa wood comes from Ecuador, where it is grown in dense plantations.
Balsa trees grow incredibly rapidly, reaching nearly 30 metres in under 15 years, but rarely live beyond 35 years.
The balsa tree is a member the Malvaceae family which contains species such as cotton (Gossypium hirsutum), cacao (Theobroma cacao) and okra (Abelmoschus esculentus).
Plant description
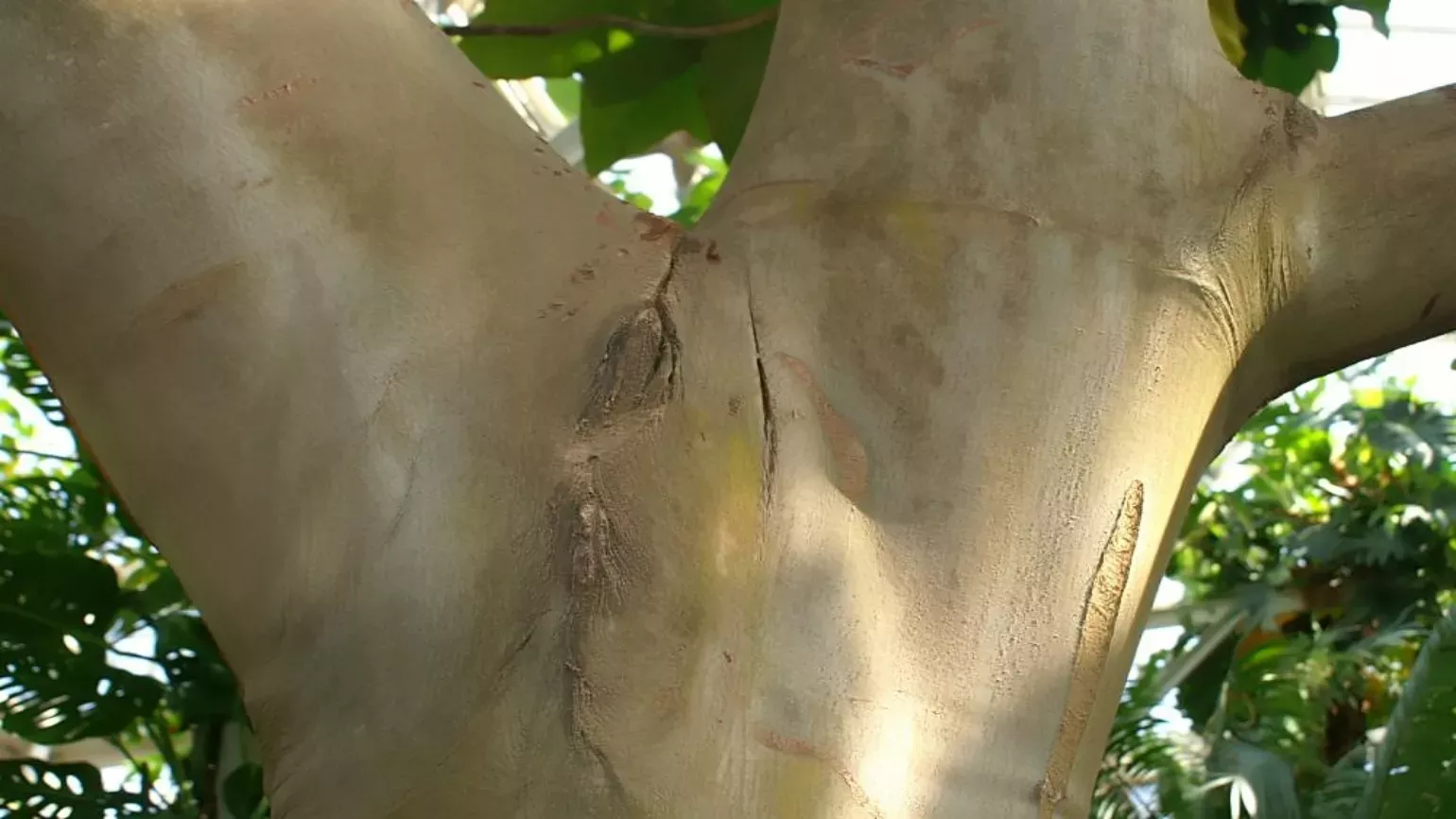
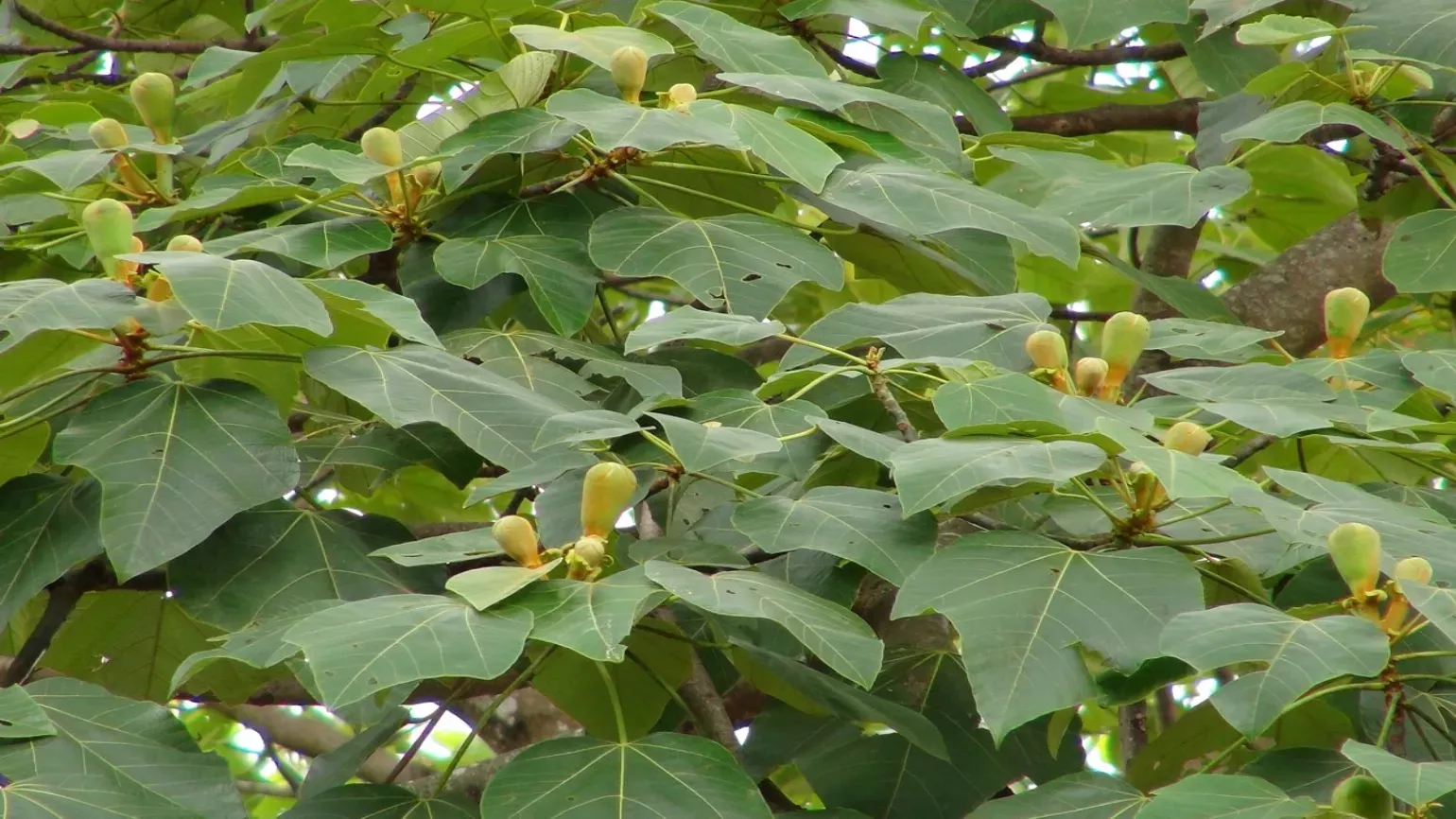
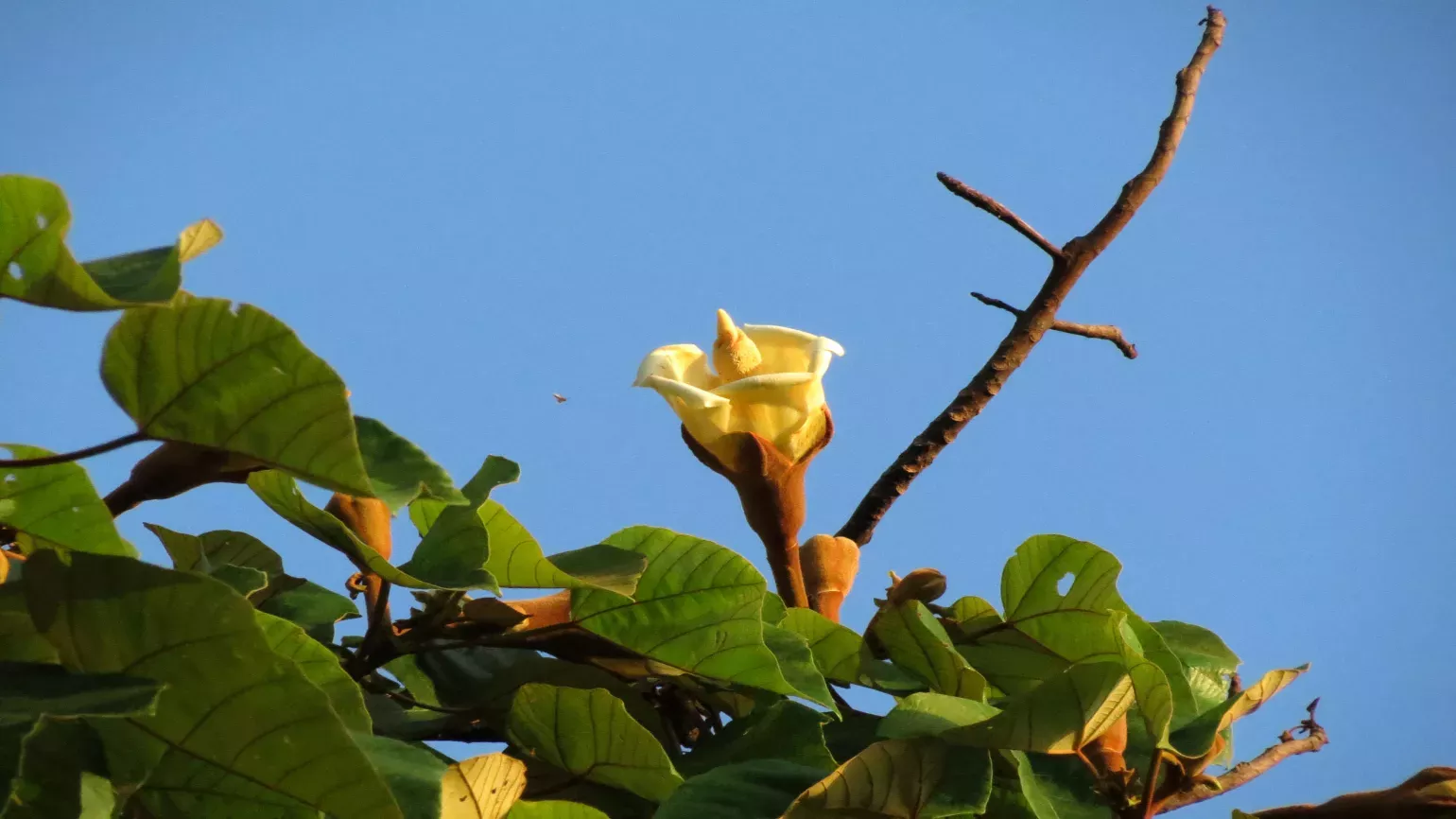
The balsa tree is a deciduous or evergreen tree with smooth, grey-white bark that grows around 40m tall. The large leaves are weakly palmately lobed, and grow 30 to 40cm across. Balsa tree fruits are green capsules with cottony filaments called kapok which surround the seeds .




Plant uses
Materials and fuels
Despite being a hardwood, balsa wood is very soft and light so it is used in crafts such as model airplanes.
Due to its buoyancy, balsa wood is also used for surfboards, buoys and fishing floats, and has been used historically for life rafts and lifebelts.
The cotton-like filaments (kapok) from the fruits can be used as stuffing in pillows and cushions.
Did you know?
The deHavilland Mosquito was a full-sized World War II aircraft renowned for having a frame built primarily of balsa wood.
The balsa tree gets its name from the Spanish word for raft because of the wood’s high buoyancy.
Even though it has incredibly light and soft wood, balsa is categorised as a hardwood because it comes from a flowering tree.
Where in the world?
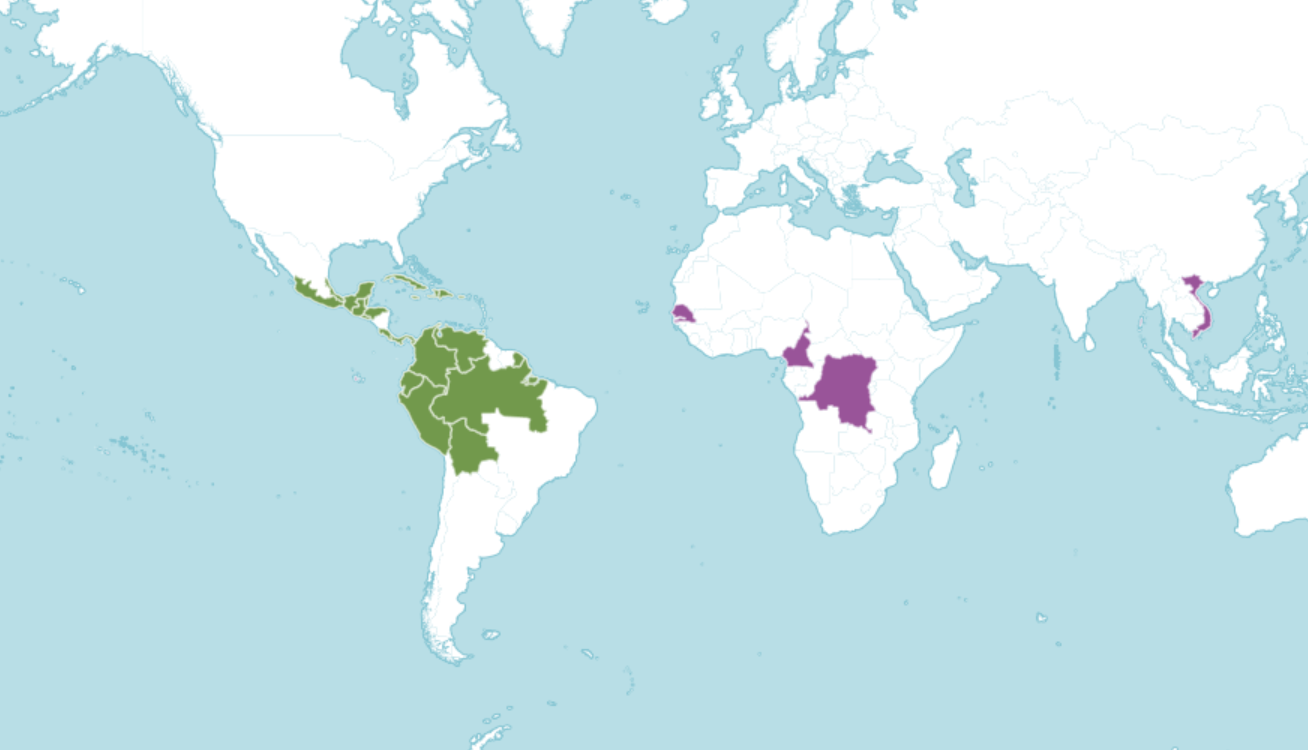
Tropical forests.