Bioimaging
Equipped with state-of-the-art instrumentation for both light and electron microscopy of plants and fungi.
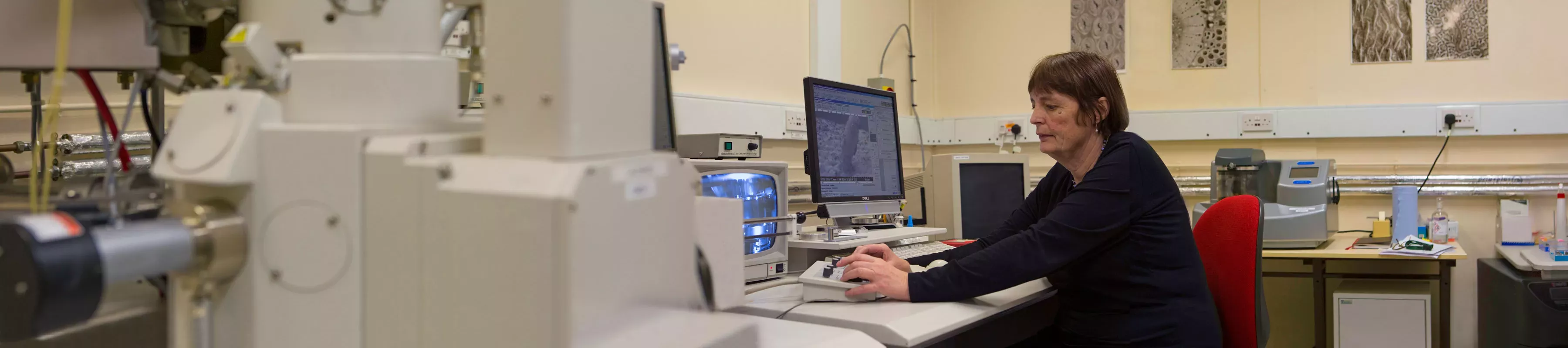

Our bioimaging facility provides state-of-the-art instrumentation and expertise to internal and external users.
Our team has specialised expertise in the equipment as well as a sound understanding of cell biology. This knowledge base allows us to provide training and guidance throughout your project, from determining the best equipment to use, to the logistics around imaging your samples themselves. We are available to help throughout all stages of your experiment.
Our overarching strategy emphasises the importance of knowledge transfer to students and researchers by providing training on as many techniques as possible. We believe the more techniques you can learn, the easier it is to identify when and where to use imaging in your science.
The facility is equipped with instrumentation for both light and electron microscopy.
Facility staff provide full training and technical support to suit your needs. From total beginners to those who are more experienced. Training is normally provided 1-to-1 at the instruments. Small groups with similar requirements can be accommodated on request.
We specialise in the imaging of plants and fungi but can also cater for a wide-range of imaging requirements for insect and animal cells. We offer advice on choice of techniques, experimental design, image interpretation and image analysis. The bioimaging facilities can be used in two ways:
- Use-it-yourself – once you are fully trained you can use the imaging facilities with ongoing technical support.
- Full service – our highly-skilled staff can provide for your imaging needs, with the emphasis on collaborative projects.
We provide:
- Routine sample preparation service, such as embedding and sectioning.
- Many specialised techniques and bespoke services.
- Various types of fixed cell imaging.
- Dedicated data analysis workstations – you can analyse your data in-house.
If a specialist technique or our extensive input is required we encourage collaboration, often resulting in a joint publication.
The bioimaging facility primarily supports the microscopy needs of Kew Science but is available to external customers, both academic and industrial.
Equipment
To book any of the Bioimaging equipment at Kew, follow the link to our booking portal.
Electron microscopy
- TEM (transmission electron microscope) and a SEM (scanning electron microscope) and specialist sample preparation equipment
- Sample preparation by a variety of techniques for TEM, such as high-pressure freezing and freeze-substitution, resin embedding and sectioning, cryo-sectioning of non-embedded material, immuno-gold labelling or negative staining
- SEM – we offer critical point drying of specimens. We also have freeze fracture cryo-SEM techniques and energy dispersive x-ray spectroscopy for elemental analysis. Our SEM has a field-emission gun, giving the highest resolution capabilities.
Hitachi H-7650 TEM
A 120 KV transmission electron microscope with AMT 2k x 2k digital camera system in a fixed bottom configuration.
The Hitachi H-7650 transmission electron microscope enables high magnification and high-resolution imaging at the subcellular level. It can be used in bright field imaging, dark field imaging and selected area diffraction mode.
It is fitted with a motorized, side entry eucentric goniometer stage allowing for electron tomography, a versatile method for obtaining 3D reconstructions from tilt series of images.
Magnification range:
50x - 1,000x in low-mag mode
200x - 200,000x in HC mode
3,000x - 600,000x in HR mode
Hitachi Regulus 8230 FE-SEM
Scanning Electron Microscope equipped with EDX.
A high-resolution, field emission scanning electron microscope with SE and BSE and STEM detectors. Low voltage (2kV) resolution is 0.7 nm in high vacuum mode. It is the perfect all-round tool for a wide range of samples.
Magnifications:
30-10,000x in Low Magnification mode
250- 2,000,000x in High Magnification Mode for secondary electron (SE)
Resolution:
0.7nm, dependent on working conditions
Image output:
8-bit and 16-bit TIFFs, up to 3072 x 2304 pixels
Detectors:
- in-lens secondary electron detector
- Semiconductor type backscattered detector
- in-lens energy and angle selective backscatter detector
- multimode scanning transmission electron microscope (STEM) detector
- energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) detector (Oxford Instruments Ultim Extreme detector)
- Our SEM regulus 8230 is also equipped with Quorum PP3010 CRYO Stage.
Light microscopy
- Conventional bright-field, phase, DIC (Nomarski), polarisation, epi-illumination and fluorescence imaging.
- Laser micro-dissection for contamination-free defined samples for downstream experiments.
Zeiss Axio Imager Z2
This system is equipped with both colour (histology) and monochrome (fluorescence) cameras. The microscope stand is upright with motorised stage control (z sectioning, time lapse, tiling and multiple positions), software auto focus.
Acquisition modalities are bright field, DIC, phase contrast and fluorescence (complete visible range). The fluorescence illumination is a Zeiss Colibri 7 LED light source giving independent control over 7 LED bands.
Leica DM6000 B
Upright, wide-field microscope with fully motorised stage and two digital cameras: a Leica DFC365 FX (monochrome) and a DFC295 (colour). Capable of bright field, polarised, DIC and fluorescence modes. Metal halide lamp for a wide range of visible and fluorescent dyes.
Leica M165FC Stereo-Fluorescence microscope
This microscope is computer controlled and can capture images using a Leica DFC450C colour camera. Imaging modalities are reflective bright field (LED light ring), transmission illumination (bright field and dark field) & fluorescence (LED illumination). It can also perform z sectioning and time lapse.
Leica LMD7 Microdissection Microscope
Laser microdissection (LMD) enables users to isolate specific single cells or entire areas of tissue. The laser and dynamic software, allows users to easily isolate regions of interest from entire areas of tissue down to single cells or even subcellular structures such as chromosomes.
LMD is typically used in genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics. Furthermore, LMD is a good tool for live cell culture, for cloning and re-cultivation, manipulation or downstream analysis.
Sample preparation
SEM sample preparation
Quorum Q150TS Sputter coater
A Quorum dual coater high resolution sputter-coater for use with our field emission SEM. Targets routinely available are Au or Pt. Can be configured for carbon evaporation for EDX analysis.
- Touch and swipe capacitive screen.
- Multiple-user profiles can be set up on one machine.
- New software sorts recipes per user according to recent use.
- Capable of achieving vacuum of 5 x 10-5 mbar
Leica EM CPD300 Critical Point Dryer
The Leica EM CPD300 critical point dryer dries biological specimens such as pollen, tissue, plants, insects, as well as industrial samples, like Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS) or Micro fluids and gels in a fully automated and controlled process. You can rely on the same high sample quality from every run. The procedure of critical point drying is an efficient method for drying delicate samples for SEM applications. It preserves the surface structure of a specimen which could otherwise be damaged due to surface tension when changing from the liquid to gaseous state.
Sectioning facilities
Reichert and RMC ultramicrotomes, conventional and cryo, for ultra-thin and semi-thin resin sectioning for both light and electron microscopy applications. We have a knife-maker (Leica KMR3) for preparing glass knives, a Leica EM Trim pyramitome for shaping resin blocks, hot-plates for drying slides, and light microscopes for checking sections, alongside a slide-staining area.
Leica Autocut RM 2155 semi-automatic rotary microtome (for wax or resin) and a Reichert-Jung rotary microtome for wax sectioning.
Sliding, sledge and cryo-microtomes. Automatic knife sharpeners for tungsten steel knives.
High pressure freezer and freeze substitution unit
A Leica EM Ice high-pressure freezer, with 3mm and 6mm carriers, used for freezing very small samples at pressures of ~2000 bar, to prevent ice-crystal growth. Sample size is extremely limited, but it can provide the best method for membrane-preservation. Due to the challenging nature of this technology, it requires technical assistance.
The Leica AFS2 for freeze substitution machine is generally used after high-pressure freezing but can also be used for the PLT embedding method (progressively lowering temperature). Both these methods have been shown to help retain antigenicity and are therefore used when immuno-gold labelling studies are required for TEM.
To book any of the Bioimaging equipment at Kew, follow the link to our booking portal.
Or scan the QR Code below

Selected publications
Rudall, P.J., (2020)
Colourful cones: how did flower colour first evolve?
Journal of Experimental Botany, 71(3), pp.759 767.
Rudall , P.J., Prychid, C.J. and Gregory, T., (2014)
Epidermal patterning and silica phytoliths in grasses: an evolutionary history.
The Botanical Review, 80, pp.59 71.
Rudall, P.J., Remizowa, M.V., Prenner, G., Prychid, C.J., Tuckett, R.E. and Sokoloff, D.D., (2009)
Nonflowers near the base of extant angiosperms? Spatiotemporal arrangement of organs in reproductive units of Hydatellaceae and its bearing on the origin of the flower.
American Journal of Botany, 96(1), pp.67 82.
Discover more
-
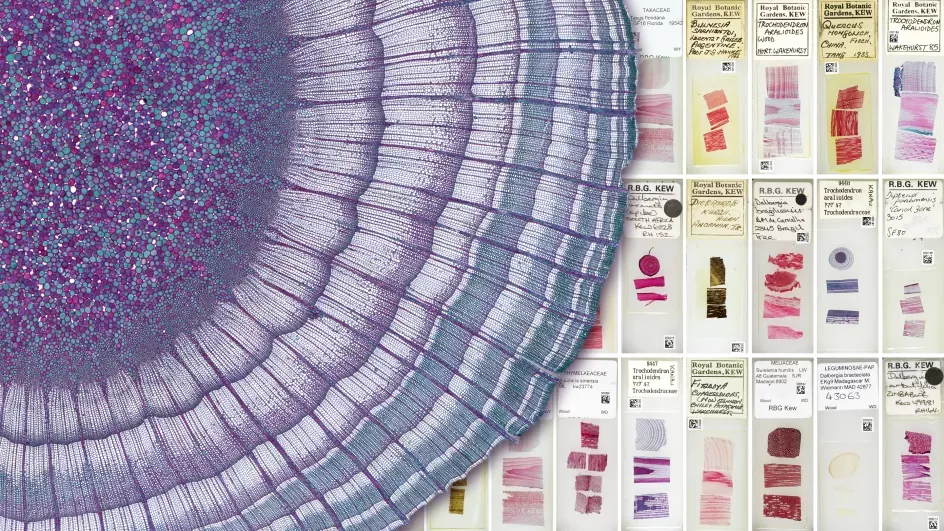

Microscope Slide Collection
Our Microscope Slide Collection holds around 150,000 specimens from a diverse range of plant taxa, particularly from seed-producing plants.
-
Wood Identification
A one-week course that teaches effective methods of recognising the distinctive characteristics of woods from different tree species.