GeoCAT help
Our help guide for using the GeoCAT tool.
1. What the tool can do
The tool provides a quick and easy way use information on the distribution of a species to help inform a conservation assessment.
- Pick a species to assess or create a new project from scratch
- Upload your own occurrence data e.g. co-ordinates of specimens, field observations or plot samples from an existing data set
- Manually add occurrence points to the map and edit them based on your own knowledge
- Import occurrence data from online sources such as GBIF or Flickr
- Single-click analysis of extent of occurrence (EOO) and area of occupancy (AOO)
- Visualise your results in Google Earth
- Download occurrence data used in the analysis
- Save your project and add more data later or share with partners in a collaboration
- View and save all the vital statistics as a mini-report
2. Getting started
See the introductory screencast on how to get started or follow the help notes below:
- Browse to the GeoCAT website
- "Start a new project" or "Import a saved .GeoCAT/.RLA file"
You can now add data to your map, analyse the distribution and determine a geographic range based conservation assessment.
3. Add data
There are three ways in which you can add data:
1. Import data
You can search existing online sources of occurrence data. At present the tool can search the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF) and Flickr, an online repository for images.
- From the 'Start your new assessment by...' window click 'Import Data'
- The 'Add new source' window will open at the right side bar
- To import data from GBIF click the 'Add points from GBIF' option, enter a name to search on and the tool will query GBIF to see if there are any georeferenced occurrence records.
- The number of occurrences is reported in the window
- Add these to the map by clicking 'import'
- If there are more than 1,000 occurrences only the first 1,ooo will be imported
- The GBIF occurrences will be displayed as green dots on the map and will display in the 'Sources' menu as 'GBIF points'
- To search Flickr for occurrences follow the same procedure, but click on 'Add points from Flickr' instead.
2. Upload data
If you have your own occurrence data in a spreadsheet or database you can import this directly. In order to upload your own data you will need to create a .CSV file. For more information on how to do this see the FAQ page.
- From the 'Start your new assessment by...' window click 'Upload Data'
- The 'Add new source' window will open at the right side bar
- To upload your data click the 'Import .GeoCAT, .CSV' option
- Click the 'Browse' button and select your .CSV file
- Your file name should appear in the window - see the troubleshooting FAQ if the file does not load
- Click the 'import' button and your points will be displayed on the map as blue dots and will appear in the 'Sources' menu as 'User points'
3. Add points
If you have knowledge on the distribution of a species then you may want to add points directly to the map.
- From the 'Start your new assessment by...' window click 'Add Points'
- The 'Add new points' button is now active so wherever you click on the map a new point will be added
- You can also search for a localities name or latitude/longitude and enter in the "go to" box top left - see below for more details
4. Map tools
Click the 'Help button' on the top right of the viewer to see what the various map tools do.
Pointer, Marquee, Add points, Delete points and Manage layers.
Undo/redo buttons.
Analysis menu.
Sources menu.
Download and Save buttons.
5. Interacting with the map editor
The tool uses the familiar Google Maps world base map with Terrain, Roadmap, Satellite and Hybrid options.
Go to search box.
If you wish to zoom to a specific location you can use the 'go to' search box. Simply add your location e.g. London and press Return/Enter or click the search button. You can also enter latitude and longitude co-ordinate pairs (e.g. 51 29' 07" N, 0 17' 30" W or 51.48528 -0.291667) directly into the search box.
Zoom bar
To quickly zoom in and out of the map you can use the zoom bar on the left hand side of the screen. You can also zoom with a double click on the left mouse button.
6. Carrying out the analysis
With your points on the map it is now possible to carry out an analysis of the geographic range of your species.
The default status is for the analysis to be disabled:
To enable the analysis click the grey square to the left of the x. The analysis is now enabled:
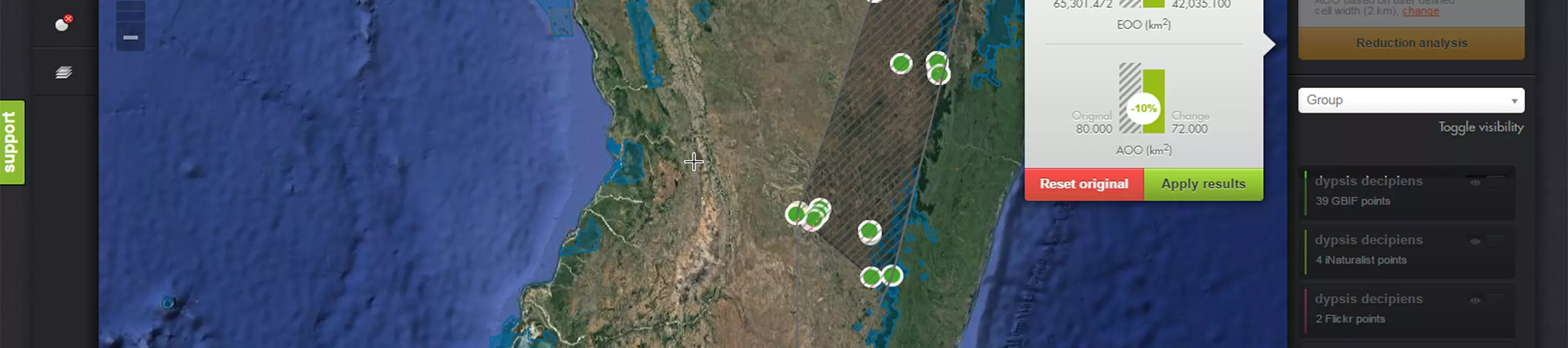
The analysis reports the two area values extent of occurrence (EOO) and area of occupancy (AOO) as well as the potential corresponding Red List Category, in this case Least Concern (LC) and Endangered (EN). For the AOO value the cell width is also reported, in this case a 2 km cell width was used.
The analysis graphics.
The example above shows a species distribution represented by eight points. The satellite map underlay has been used to help illustrate the forest cover. The shaded area between the points, within a black line, represents the extent of occurrence (EOO) (based on a convex hull) and the red grid cells represent the area of occupancy (AOO).
For more information on these values please see the Analysis section of the FAQ.
7. Report
To record your findings there is an option to create a report. Click on 'Print complete report' and your results will be displayed in an HTML page with a map. The page can be printed or saved as a PDF if you have the appropriate software. Note that the map in the report is still under development.
8. Save your project with the .GeoCAT file
You can save your data by clicking the green 'save project' button at the bottom of the page. This will create an .GeoCAT file which retains all the information about the analysis you have been working on including the points added and even the zoom level of the map. Depending on the browser you are using you will either be asked for a location in which to save the file or it will automatically save to your designated 'downloads' folder. If you are not sure where the file saved you can carry out a search for the .GeoCAT extension.
The download/save options
If you click the 'Close tool' button in the top right hand corner of the window and you have not saved your work you will be reminded and given the option to save your project:
If you exit without clicking 'Close tool' you will lose your work.
9. Reload your project with the .GeoCAT file
To reload your project you can upload your .GeoCAT/.RLA file in two ways:
1. From the front page
Click the 'Import a .GeoCAT/.RLA file' button and browse to your previously saved file. Click on the file and it will restore the project.
2. From the sources menu
Another way (also a good way to merge two or more datasets) is to add your .GeoCAT file via the sources menu. Click on 'Add new source' and select 'Import .GeoCAT, .CSV'. Browse to the file and select it. The file will be added to the source menu and by clicking the 'import' button the project will be restored.
10. Saving the occurrence data used for the analysis
The occurrence data will be included as part of the .GeoCAT file, however you may want to download this separately. Click the 'Download data' button, choose one of the two options to save the occurrence data:
-
Download .CSV
You can download the points in your map as a .CSV file that can be opened in may packages e.g. Microsoft Excel. Just click the 'Download CSV' option.
-
Data download options
Download .KML
By clicking the 'Download KML' option you can view your data in other packages such as Google Earth. The .KML file also includes the analysis graphics (if analysis has been enabled) as well as the analysis results.
11. Layers
A standard set of data layers are available to add to the map to aid your analysis. For more information on example layers see the layers page.
How to use layers:
Click the layers button to open the layers window.
Open layers
Click 'Add' to activate a layer.
12. Feedback
We would love to hear what you think about the tool and any suggestions you may have to improve it. You can contact us via email at GISUnit@kew.org