GeoCAT data layers
Find out more about KML/KMZ data layers in GeoCAT.
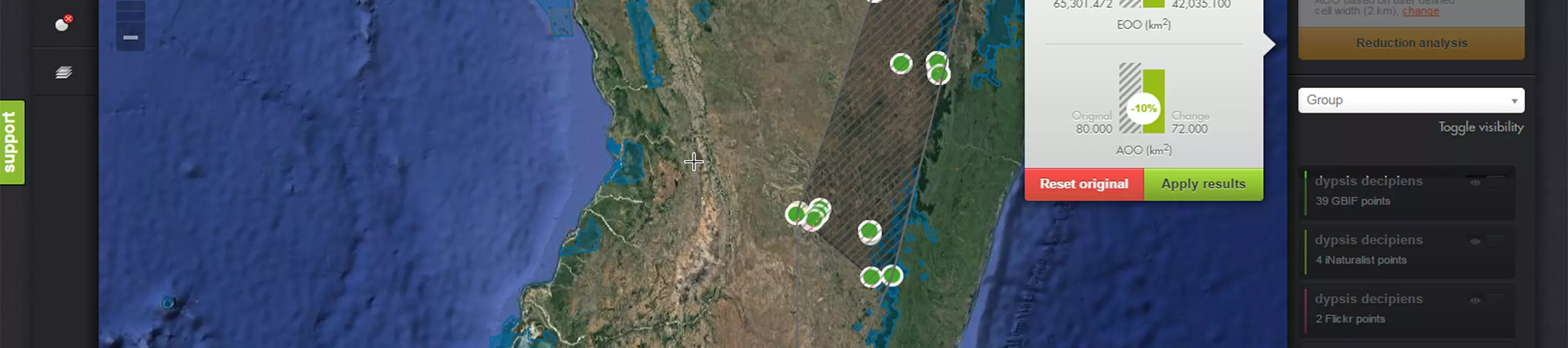
Overlaying data layers allows you to understand more about what is happening across the distribution of your species. Maps of deforestation can be particularly useful for Red List conservation assessments.
There are two options for the addition of data layers or 'overlays' to GeoCAT: Core layers and User layers. Core layers are default layers that have been built in to GeoCAT. User layers are any KML/KMZ layers that have been added by the user. This can be user generated files or data that has been posted online from an external source.
Core layers (presently only Protected Planet)
Protected Planet - http://www.protectedplanet.net/
The latest initiative harnessing the World Database on Protected Areas
Human Footprint - http://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/wildareas/
Human influence is a global driver of ecological processes on the planet, on par with climatic trends, geological forces, and astronomical variations. The Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) and the Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) at Columbia University have joined together to systematically map and measure the human influence on the Earth’s land surface today.
WWF Ecoregions - http://www.worldwildlife.org/science/ecoregions/item1267.html
A New Map of Life on Earth - Over the past eight years WWF's Conservation Science Program (CSP) has developed a biogeographic regionalization of the Earth's terrestrial biodiversity. We term our biogeographic units ecoregions, which we define as a relatively large units of land or water containing a distinct assemblage of natural communities sharing a large majority of species, dynamics, and environmental conditions. Ecoregions represent the original distribution of distinct assemblages of species and communities.
Global Forest Loss 2000-2005 - http://globalmonitoring.sdstate.edu/projects/gfm/
This dataset represents 2000-2005 gross forest cover loss. A separate regression estimator (i.e. separate regression models and parameter estimates allowed for each stratum) and post-stratification were employed to estimate Landsat-calibrated forest cover loss area. For sample blocks with intensive change a simple linear regression model was applied using the proportion of area within the sample block classified as MODIS-derived forest loss as the auxiliary variable. For low-change blocks post-stratification based on VCF tree canopy cover was implemented to partition blocks into areas of nearly zero change and areas of some change. The forest cover loss area estimates were then constructed from the sample mean Landsat-derived clearing within post-strat.
Example user layers
Fire occurrences derived from the MODIS sensor: https://fsapps.nwcg.gov/googleearth.php
Direct link for GeoCAT (current fire detections): https://fsapps.nwcg.gov/data/kml/conus_latest_modis.kml
Oil spills: http://earth.tryse.net/oilspill.html
Direct link for GeoCAT: http://earth.tryse.net/Oil_Spills_nw.kmz
How to prepare KML/KMZ layers for inclusion in GeoCAT
Not all KML/KMZ files will work in GeoCAT. Ads a general rule, if the file can be displayed in Google Maps then it should display in GeoCAT. Further notes on how to prepare your KML/KMZ files for use in GeoCAT will be coming soon...