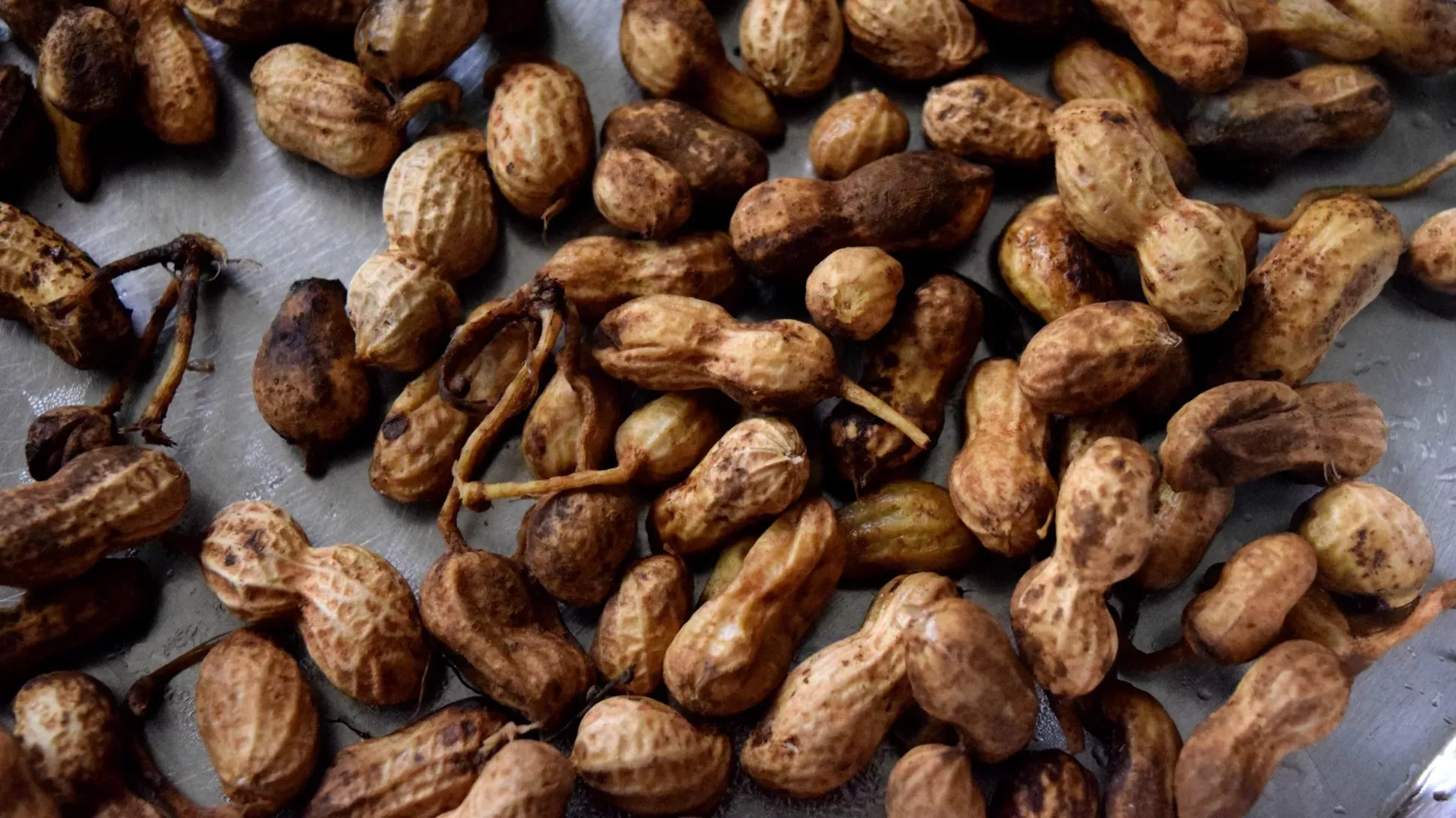

Peanut
Did you know the most popular nut in the world isn’t actually a nut?
In fact, the peanut (Arachis hypogaea) is more closely related to peas than nuts.
As members of the Fabaceae family, peanuts are technically a legume, meaning their closest cousins are plants like the common bean, lentils and chickpeas.
As well as being enjoyed as a snack, peanuts are packed with proteins, healthy fats, vitamins and minerals.
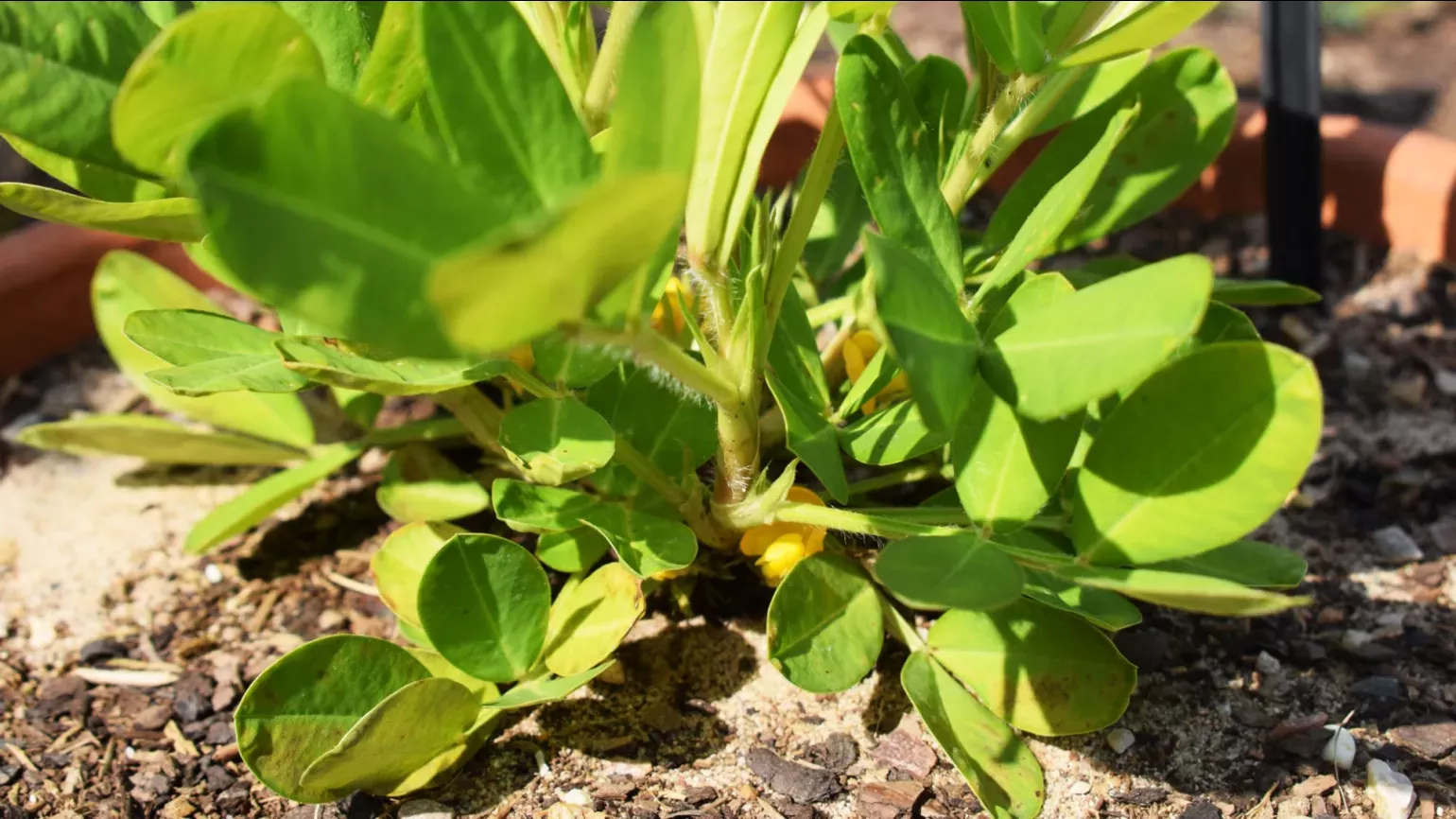
When a peanut flower is pollinated, the stalk elongates to bury itself in the soil where the seed develops, pre-planted, in a process known as 'geocarpy'.
Plant description
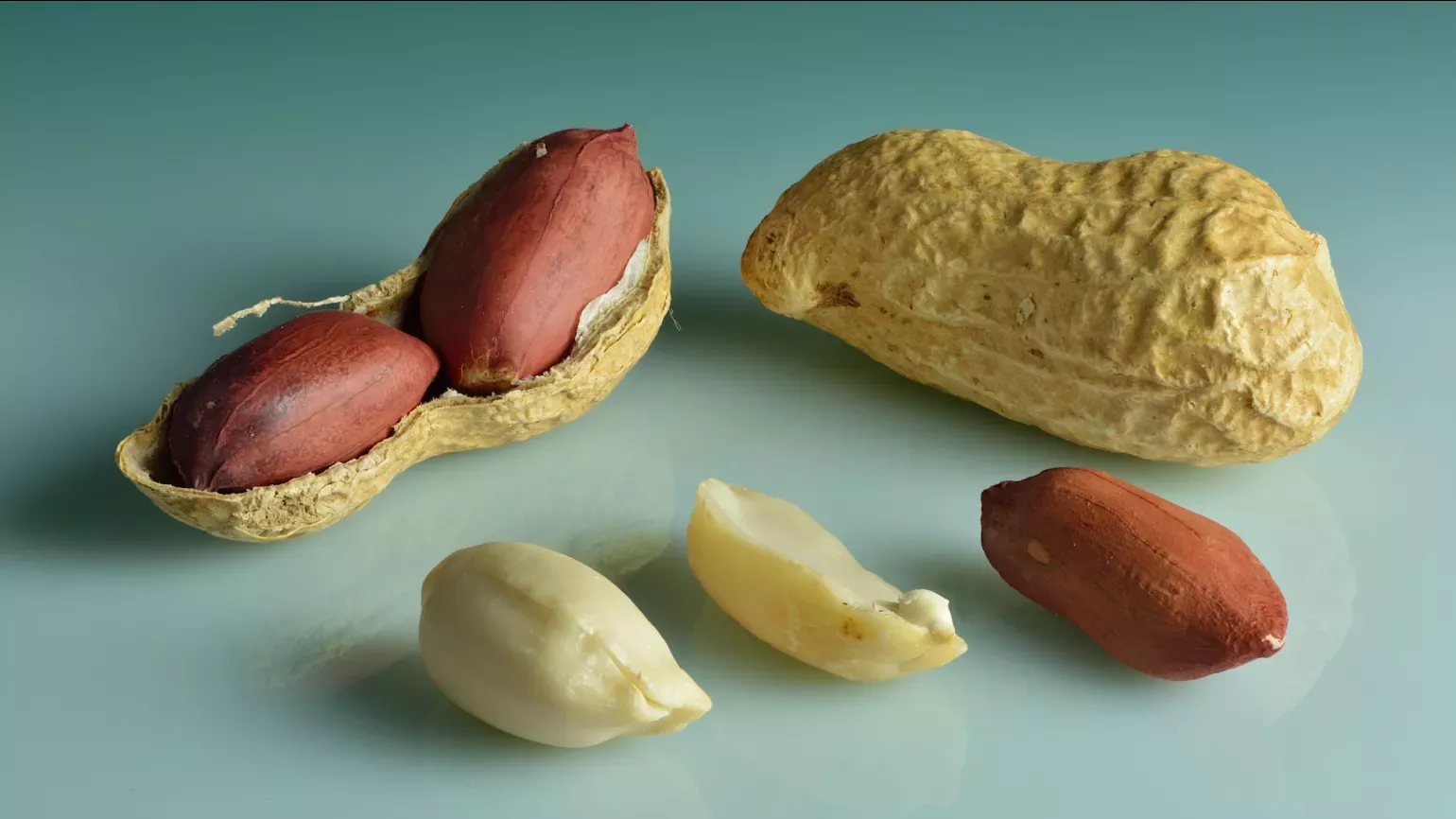
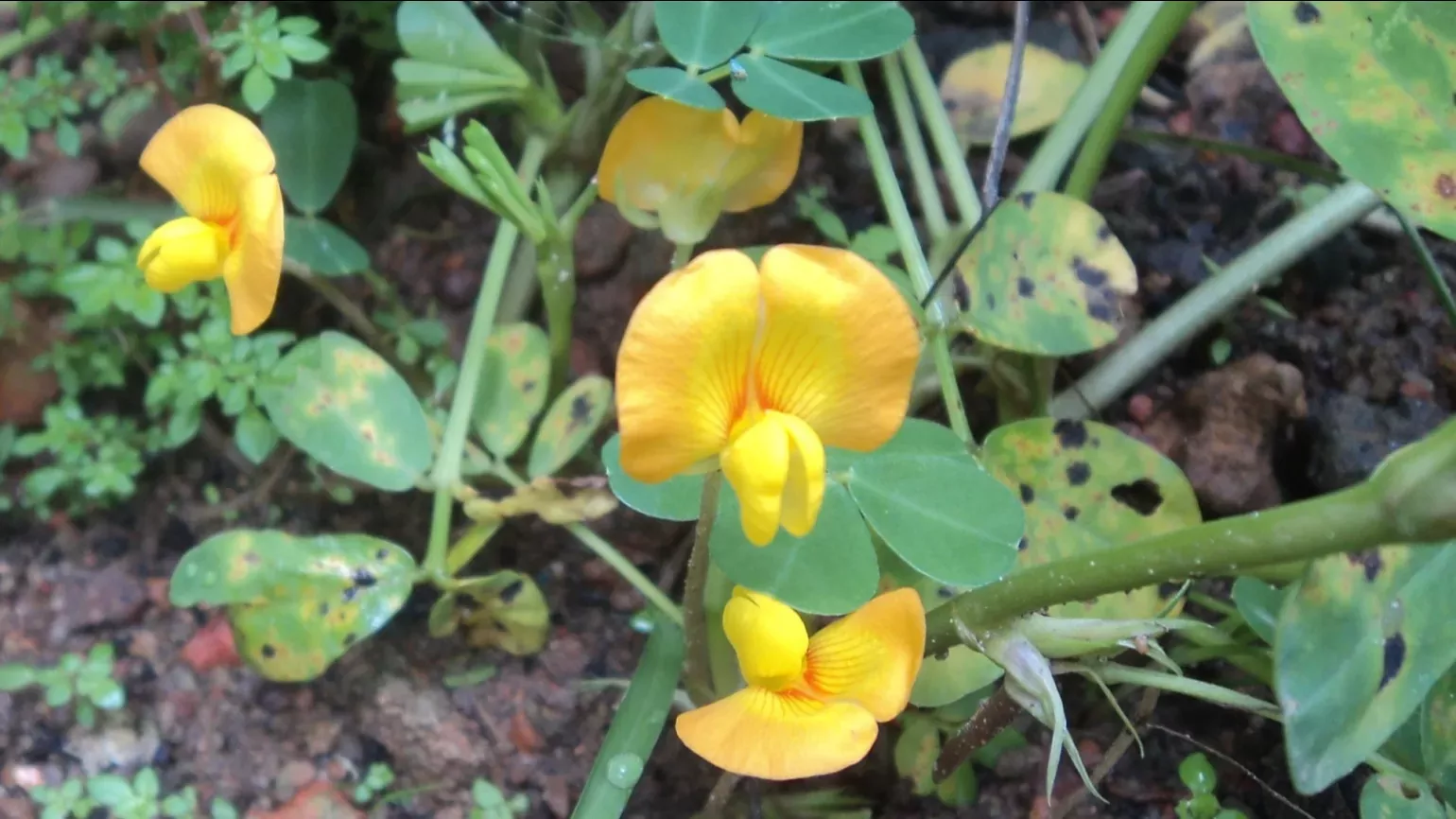
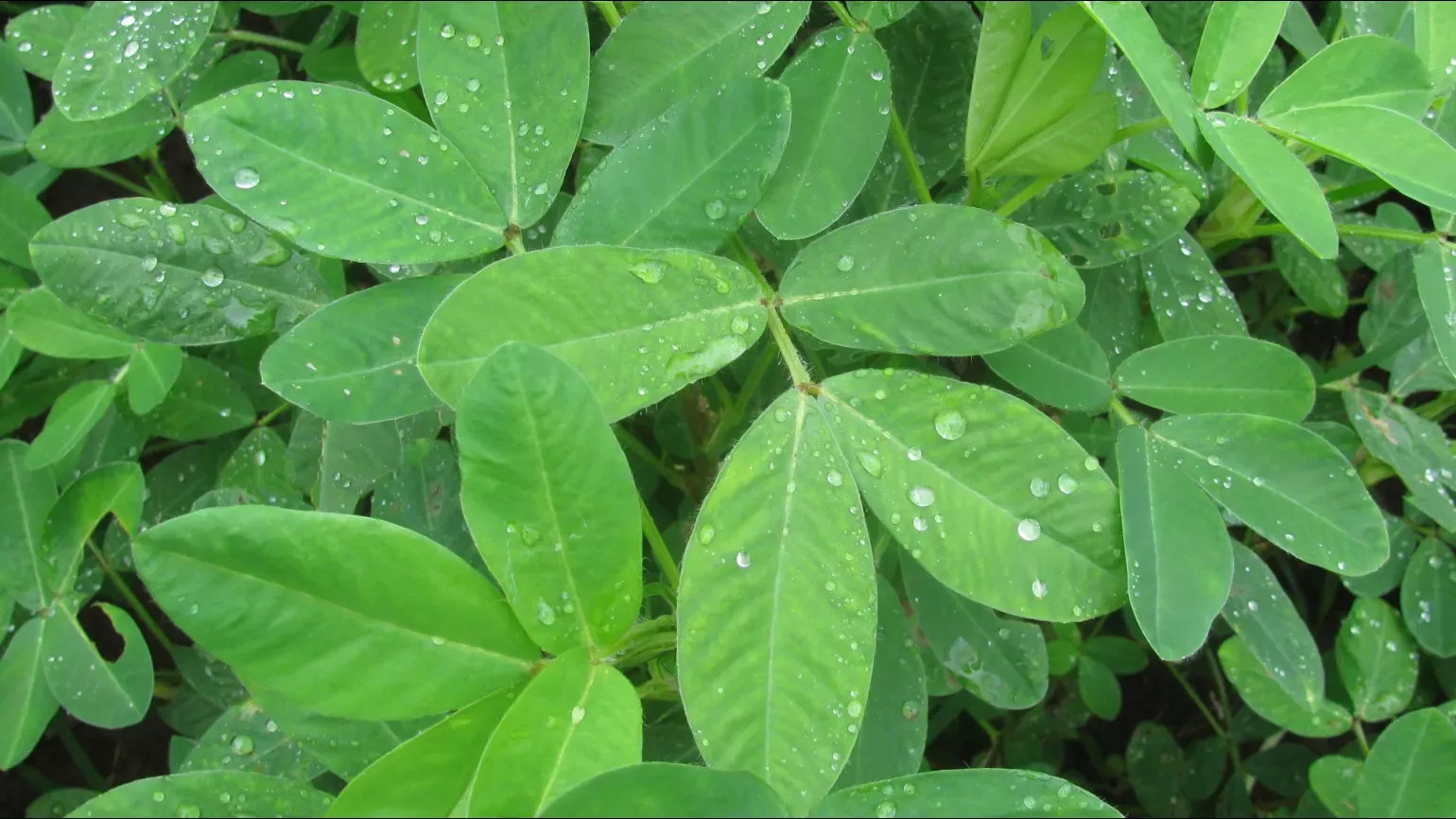
Peanut plants grow as a bush up to 50cm tall and wide. The leaves are made of four smaller leaflets, which are oval shaped and between 1 to 7cm long. The flowers are small, loosely resemble butterflies, and can be red to orange to yellow. The seeds grow underground, surrounded by an outer pod.




Plant uses
Beauty and cosmetics
Peanut oil is used in the production of some soaps and cosmetics.
Food and drink
Peanuts are commonly eaten as a snack, either raw, roasted or boiled.
Peanut butter is made from dry roasted peanuts sometimes mixed with fats and sugars.
Peanuts are used in savoury dishes, often to make a sauce served with meat.
Peanuts are also processed to produce peanut oil, which is commonly used for cooking, and peanut milk.
Health
Peanuts are an excellent source of protein, monounsaturated fats and multiple vitamins and minerals.
Materials and fuels
The leftover material from creating peanut oil can be used as animal feed.
Did you know?
Peanut allergies are the result of proteins in the peanuts accidentally trigging the human immune system.
The species name of hypogaea means ‘under the earth’, referring to where peanut seeds grow.
The modern peanut plant is actually a natural hybrid of two wild peanut species that were domesticated in South America over 7,500 years ago.
Where in the world?
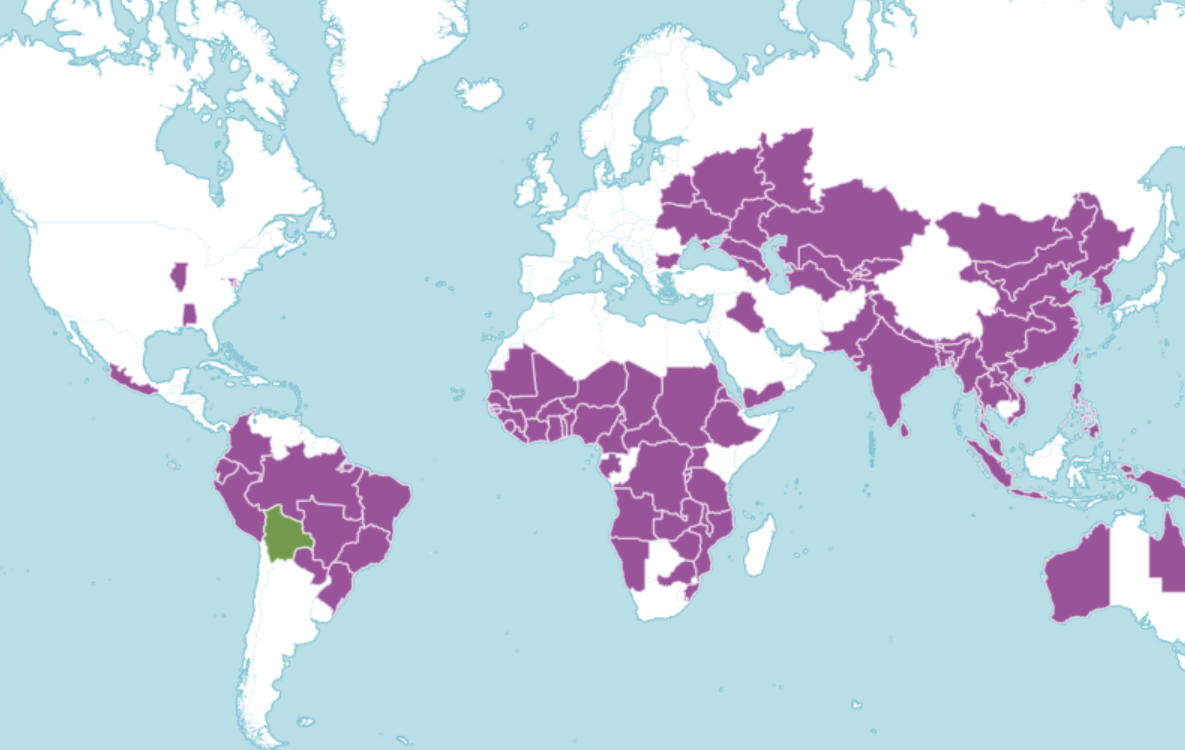
Light sandy soil in temperate regions, wildly cultivated





