Edible fig
On this page
Over 11,000 years ago, the fig became what was probably the first cultivated fruit in human history.
Today, more than 1.3 million tonnes of figs are produced worldwide, mostly coming from the ancestral home of the fruit: the Middle East.
Fig plants were first introduced to Britain during the Roman era, and still grow as ornamentals in parks and gardens across the country.
Plant description
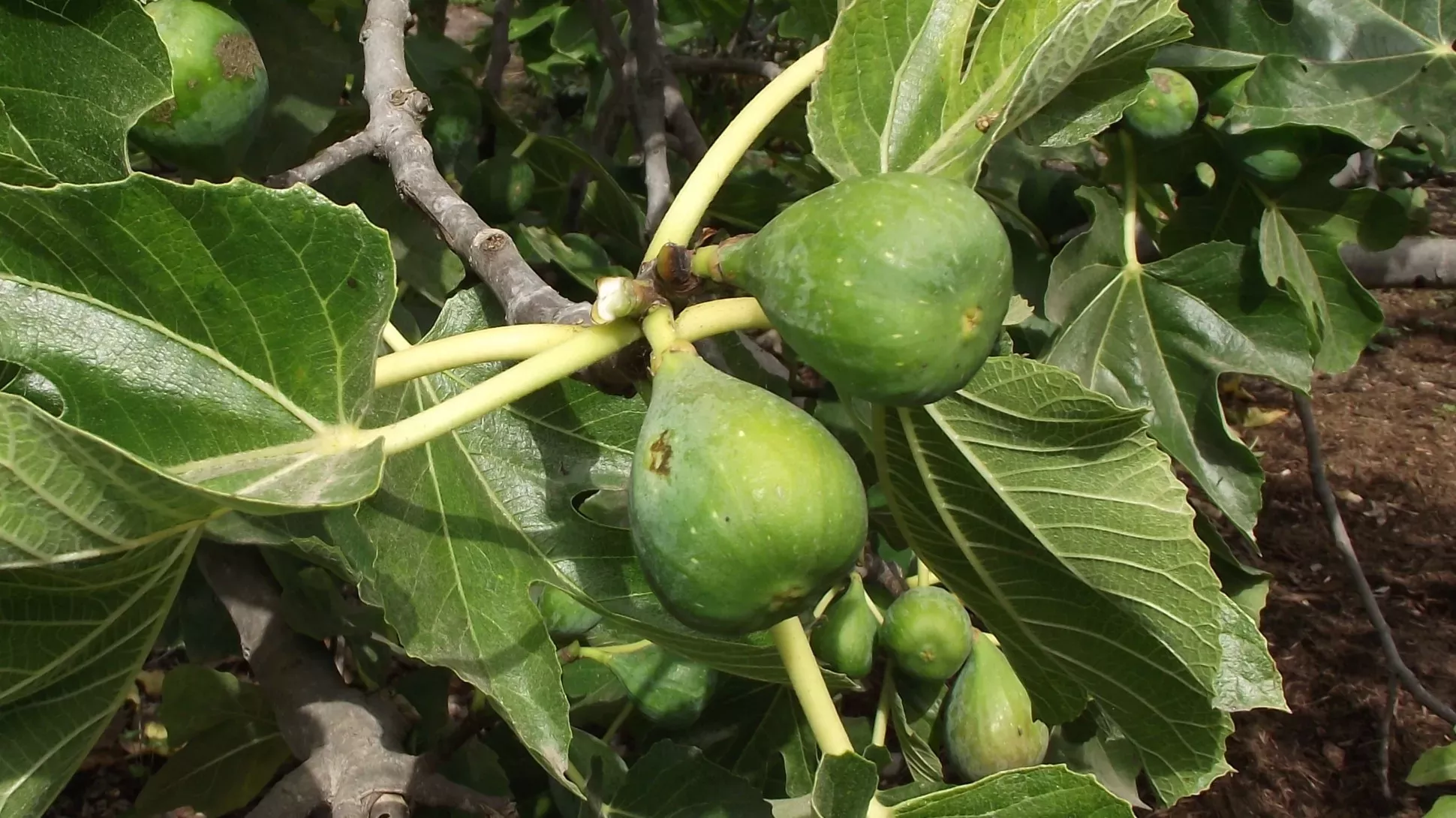
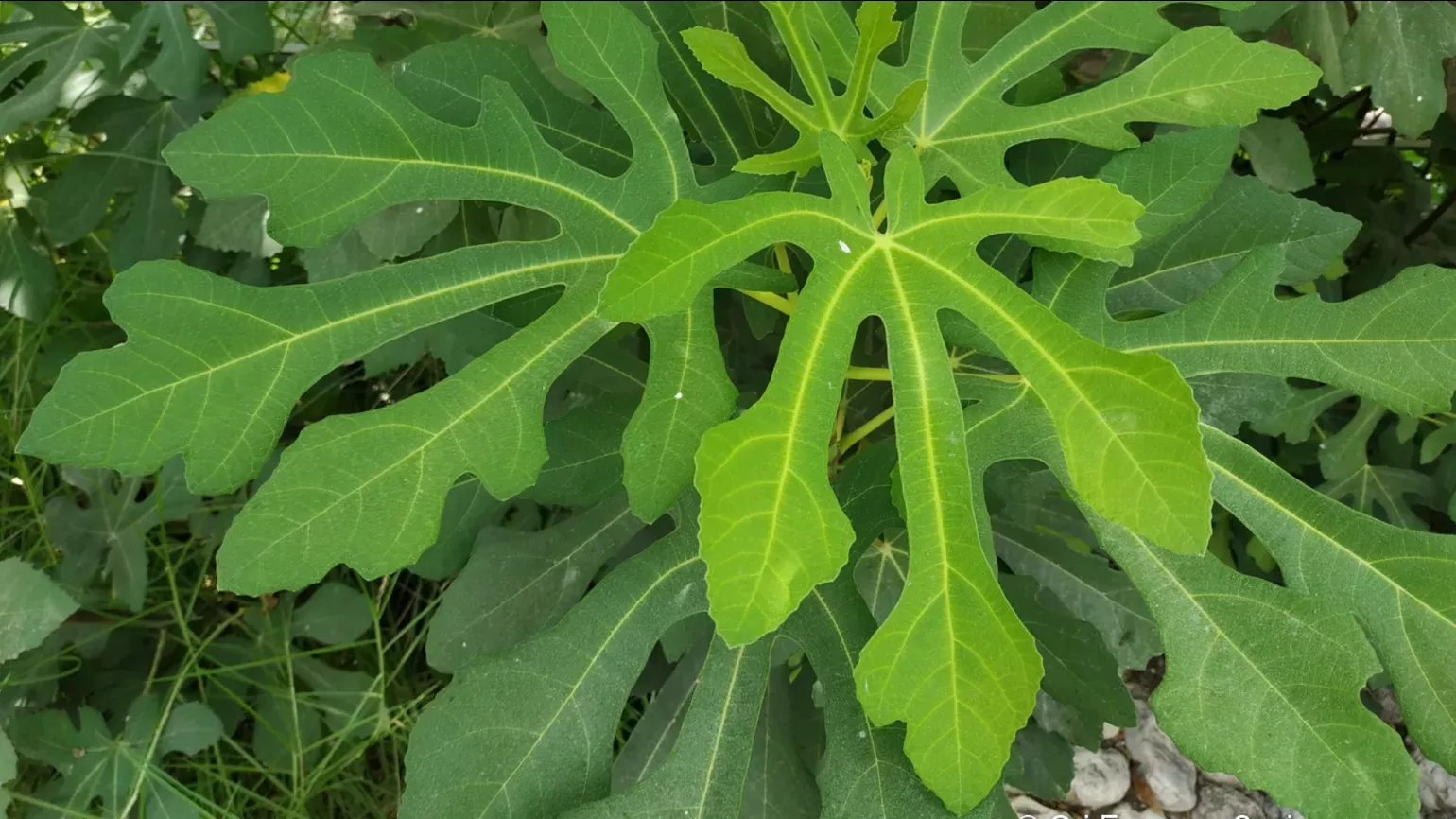
Fig leaves are around 20 cm long and 14 cm wide, with 3 to 5 deep lobes and rough to the touch.
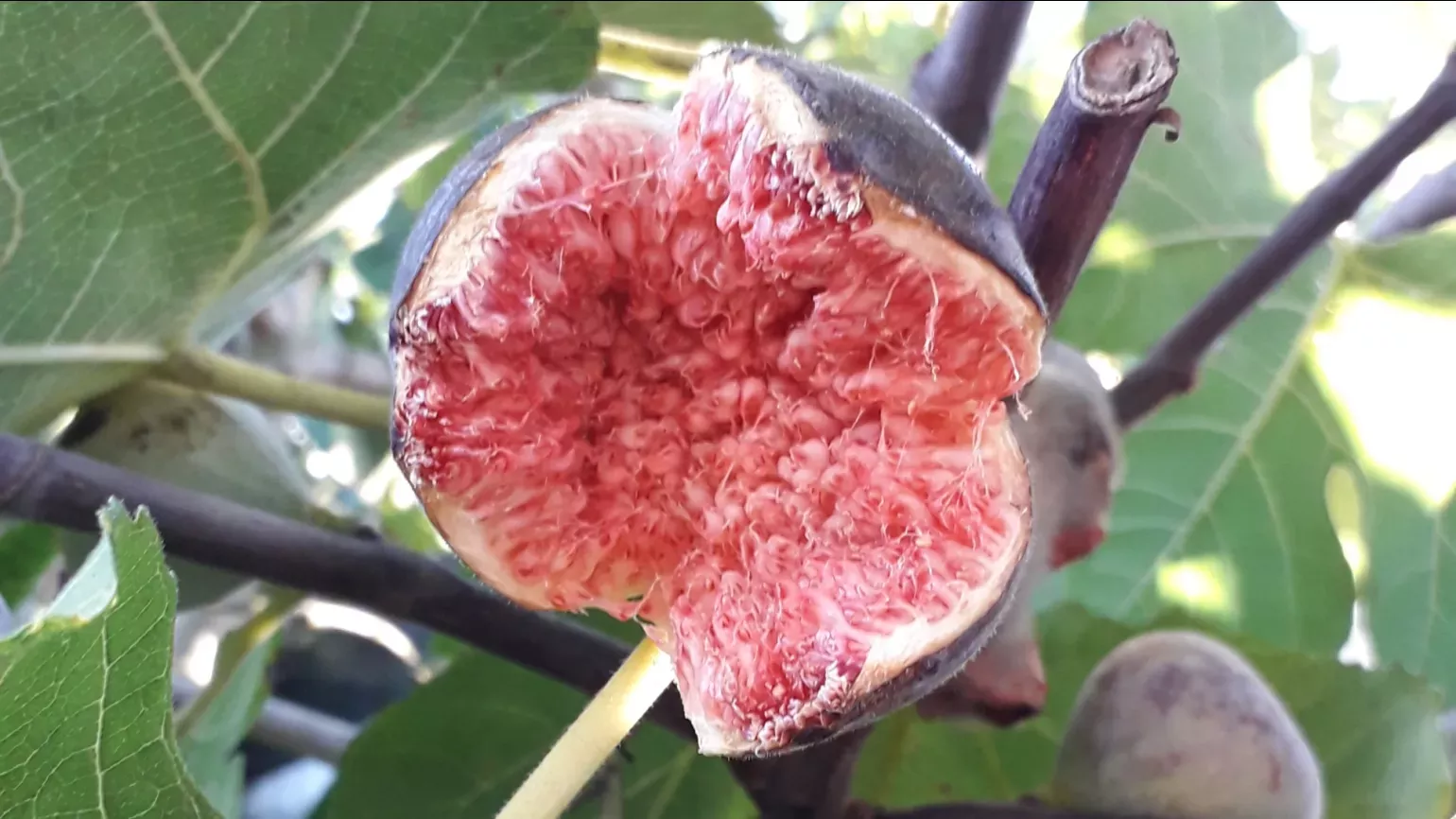
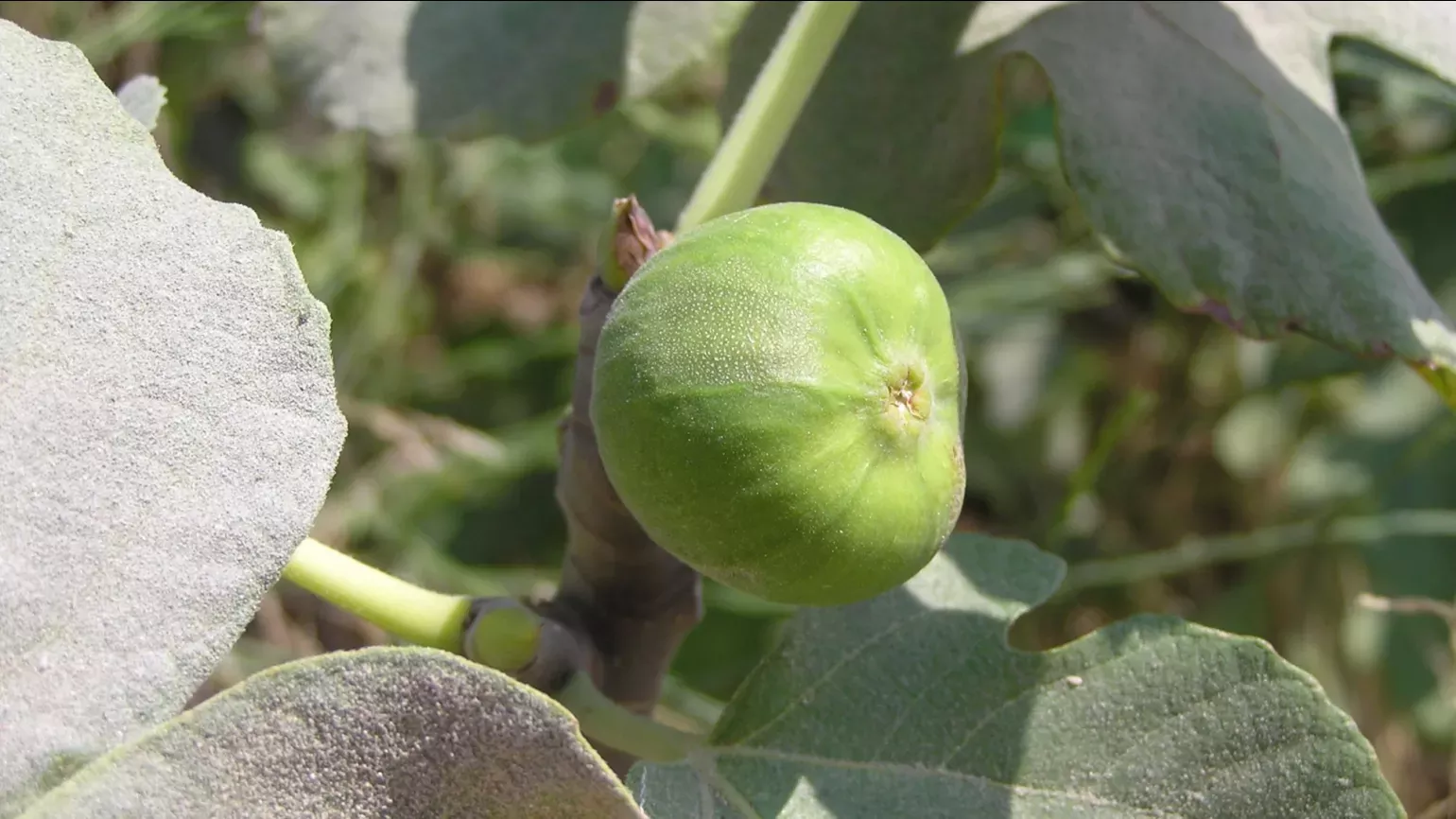
The flowers are very small and contained in a hollow fleshy receptacle that resembles an unripe fig called the synconium. The synconium has a small opening at the apex that allows a fig wasp (Blastophaga psenes) to enter and pollinate the flowers within. The edible fruit consists of the mature syconium containing numerous one-seeded fruits. Mature figs are 3 to 5 cm in diameter, with a green skin, ripening to purple or brown.





Plant uses
Cultural
The fig was described by the Prophet Muhammad as ‘a fruit that descended from paradise’, and eating them can ‘prevent hemorrhoids, prevent piles and help gout’.
The fig is one of the potential candidates for the forbidden fruit eaten by Adam and Eve in the Garden of Eden.
Food and drink
Figs are eaten raw, but are also processed into jams and fillings for sweet treats.
Figs, raw or cooked, are often paired with goat's cheese.
Health
Dried figs are a rich source of dietary fibre and manganese.
In traditional Mediterranean medicine, the sap from figs was used as a treatment for warts and calluses.
Did you know?
In the Quran, the fig is described as being a ‘perfect’ fruit, as it contains no pits of any kind.
Fig trees are gynodioecious, meaning they are either female, or hermaphroditic, although only the female tree will produce ripened, edible figs.
The sap of the fig plant can cause a skin inflammation if exposed to sunlight in a phenomenon called phytophotodermatitis.
Where in the world?
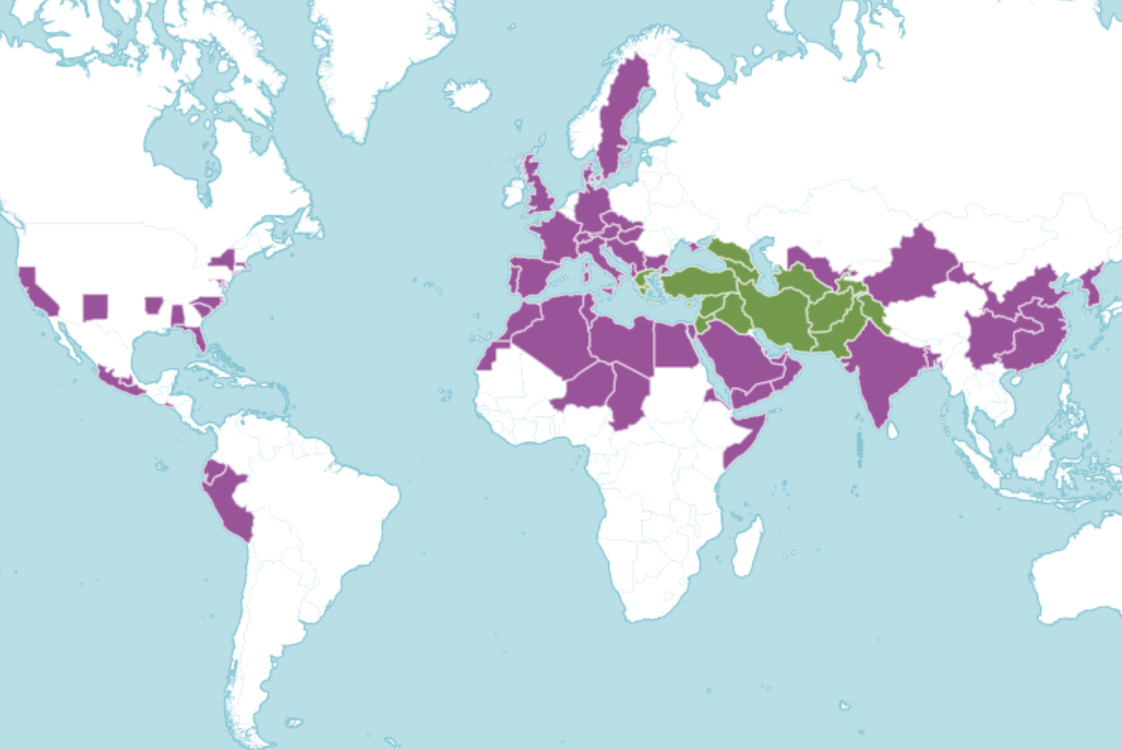
Thrives in warmer environments, in a wide variety of soil types.
Find it in our gardens
Kew Gardens
A botanic garden in southwest London with the world’s most diverse living plant collection.








