Bitter orange
On this page
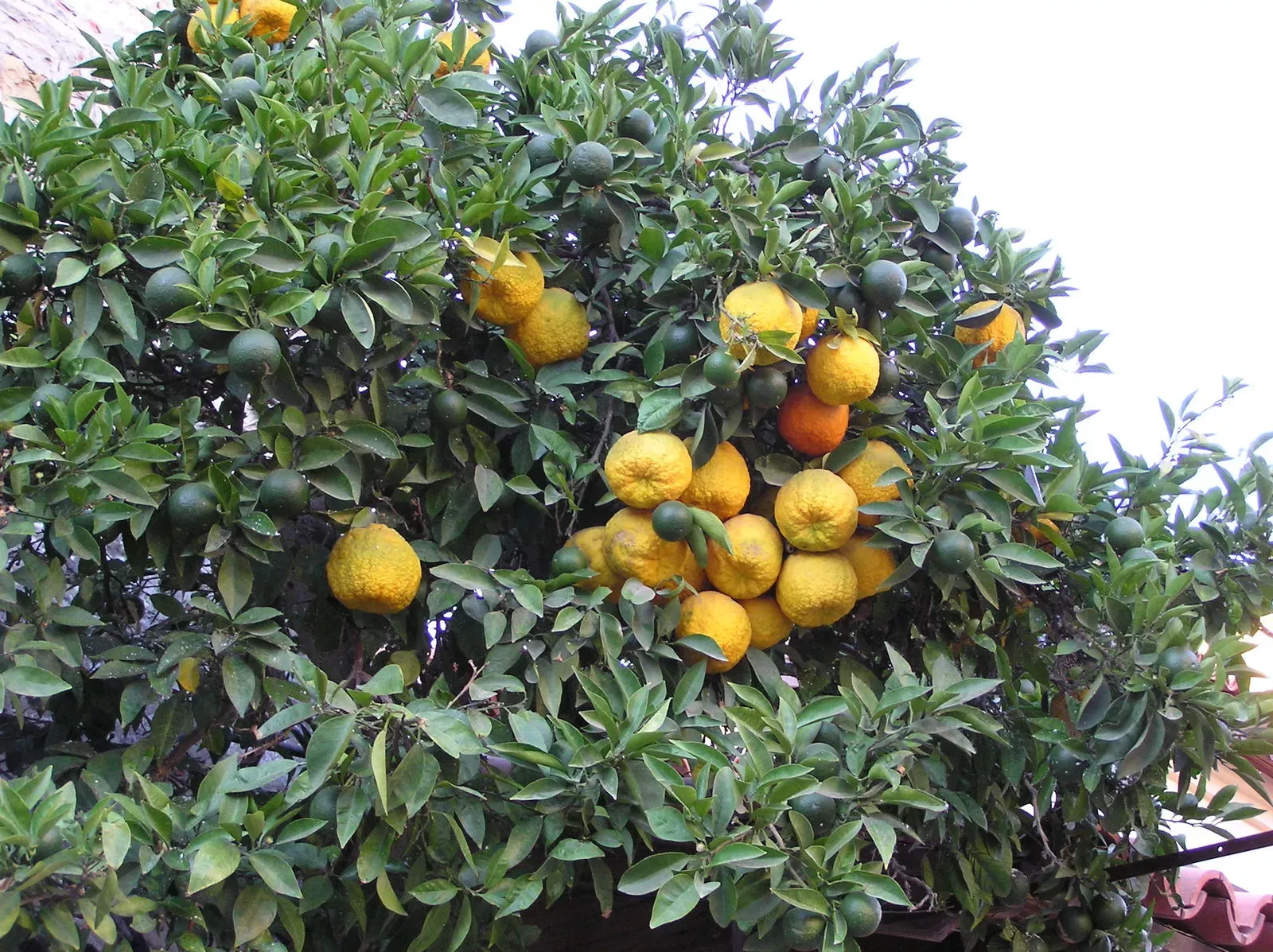
Bitter orange is an evergreen tree cultivated throughout the world for its round, orange or green fruit.
These prized fruits are a vital ingredient in marmalade and liqueurs such as Triple Sec.
Plant description
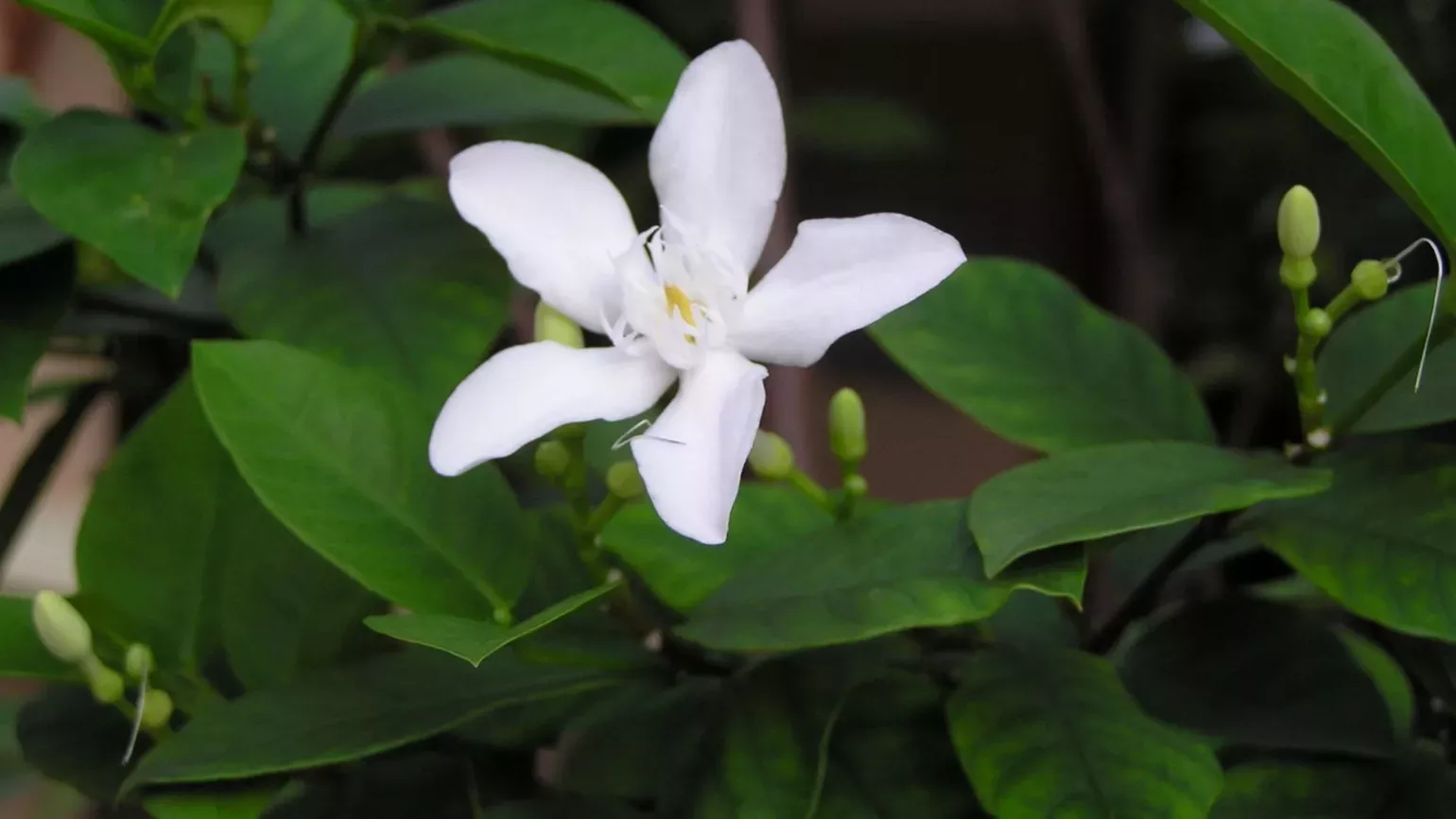
Evergreen tree with small thorns; broad, green leaves; and large, white, fragrant flowers. Its spherical fruit have a thick, orange or sometimes green peel. The juicy pulp is orange in colour and can taste sweet or sour.


Plant uses
Beauty and cosmetics
Bitter orange essential oil is used in skin care products because of its antibacterial, antifungal, antiseptic, and anti-inflammatory properties. Bitter orange is also used to fragrance perfume and hair care products with notes of citrus.
Food and drink
The raw pulp of bitter orange is inedible, but the fruit is used to make marmalade and was in early recipes of duck à l’orange.
Bitter orange oil is also used as a flavouring agent in foods and liqueurs and the fruit peel is used as a seasoning.
Did you know?
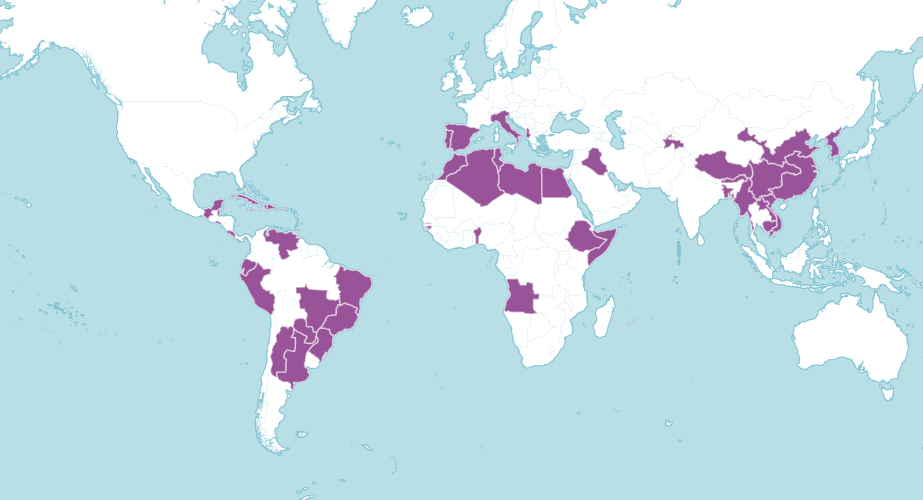
Bitter orange is an artificial hybrid - it was produced by breeding two different plants together. So it does not have a native range but it is widely cultivated throughout the world.
Where in the world?
Find it in our gardens
Kew Gardens
A botanic garden in southwest London with the world’s most diverse living plant collection.
Location
North Wing of the Temperate House
View map of Kew Gardens




